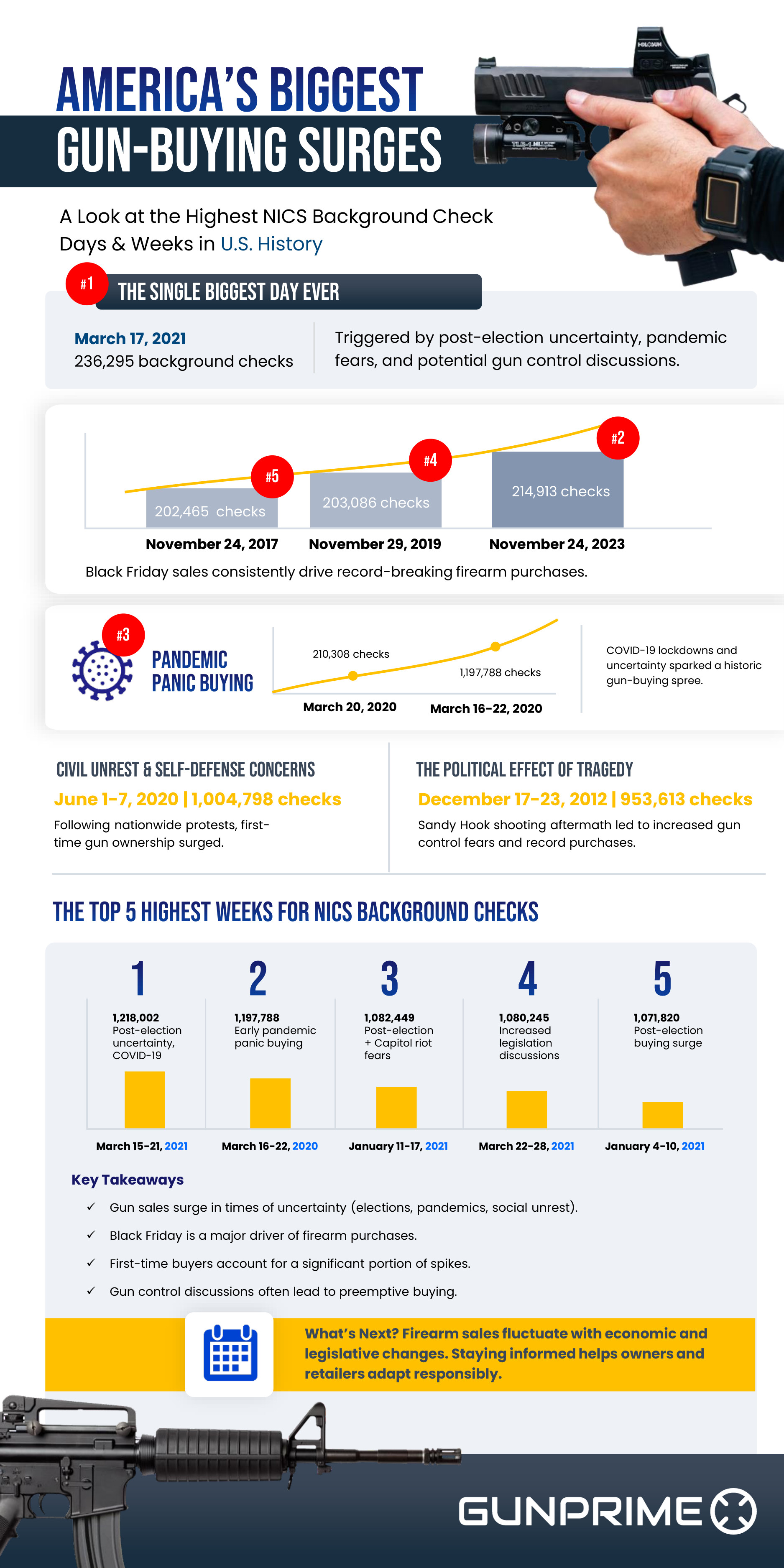
An article by GunPrimeLLC
Photo source-Shotgun Shell Photos, Download The BEST Free Shotgun Shell Stock Photos & HD Images (pexels.com)
An Overview of Shotgun Shells
Shotguns have long been a popular choice among hunters, sport shooters, and home defense enthusiasts. These versatile firearms are known for their power and effectiveness, and one crucial component that makes them work is the shotgun shell. In this blog post, we will provide a comprehensive overview of shotgun shells, covering everything from their different types to how they work and how to choose the right one for your needs. We will also delve into important topics such as safety and proper storage of shotgun shells. So, whether you are a seasoned shotgun enthusiast or just starting to explore this fascinating world, this blog post will serve as a valuable guide to understanding and utilizing shotgun shells effectively. Let's dive in!
Understanding the Basics: What are Shotgun Shells?
Shotgun shells are the ammunition used in shotguns. They are cylindrical in shape and contain all the necessary components for firing a shotgun. When loaded into the shotgun's chamber, the shell is ignited, propelling various projectiles towards the target. Let's explore the key components and features of shotgun shells in more detail:
1. Components of a Shotgun Shell
a. Hull or Casing:
The hull or casing is the outermost part of the shotgun shell. It is typically made of plastic or metal and serves as the container for all the other components. The hull provides structural integrity and protects the internal components from damage.
b. Primer:
The primer is a small, sensitive explosive located at the base of the shotgun shell. When struck by the firing pin of the shotgun, the primer ignites, initiating the firing process.
c. Gunpowder:
Gunpowder, also known as propellant or powder charge, is a mixture of chemicals that burns rapidly when ignited. It is responsible for producing the necessary pressure to propel the projectiles out of the shotgun barrel.
d. Wad:
The wad is a crucial component that separates the gunpowder from the projectiles. It acts as a gas seal, preventing gas leakage and ensuring consistent propulsion. Wads can be made of different materials, such as plastic or fiber. Photo source-https://www.pinterest.com
e. Shot or Projectile:
Shotgun shells can contain various types of projectiles, depending on the intended use. The most common type is birdshot, which consists of small pellets used for hunting birds or small game. Buckshot is another popular choice, containing larger pellets primarily used for self-defense or hunting larger game. Slugs, on the other hand, are solid projectiles designed for increased accuracy and penetration over longer distances.
2. Gauges and Sizes of Shotgun Shells
Shotgun shells come in different gauges and sizes. The gauge refers to the internal diameter of the shotgun barrel. The most common gauges are 12, 20, and .410, with 12-gauge being the most widely used. The gauge determines the size of the shotgun shell that can be used in a particular shotgun.
Shotgun shell sizes are denoted by numbers, with larger numbers indicating smaller shot sizes and vice versa. For example, #8 shot is smaller than #4 shot. The appropriate shot size depends on the intended use, such as hunting birds or larger game.
Understanding the basics of shotgun shells is essential for anyone who owns or plans to use a shotgun. By familiarizing yourself with the components and different types of shotgun shells, you can make informed decisions when selecting ammunition for your specific needs. In the next section, we will explore the various types of shotgun shells in more detail.
Different Types of Shotgun Shells
Shotgun shells come in different types, each designed for specific purposes and applications. Let's take a closer look at the three main types of shotgun shells commonly used:
1. Birdshot
Birdshot shells are primarily used for hunting birds and small game. They contain multiple small pellets, usually made of lead or steel. The pellets spread out upon leaving the shotgun barrel, increasing the chances of hitting a moving target. Birdshot is available in various sizes, with smaller shot sizes (higher numbers such as #7 or #8) being suitable for smaller birds and larger shot sizes (lower numbers such as #4 or #6) for larger birds or game.
2. Buckshot
Buckshot shells are loaded with larger pellets, typically made of lead or sometimes steel. These shells are commonly used for self-defense and hunting larger game, such as deer or wild boar. Buckshot pellets are larger in diameter than birdshot pellets, providing increased stopping power and penetration. The most common buckshot shell size is 00 (pronounced "double-aught") with approximately nine pellets per shell, but variations with fewer or larger pellets are also available.
3. Slug
Slug shells are designed for increased accuracy and long-range shooting. Unlike birdshot or buckshot, which contain multiple pellets, slug shells have a single solid projectile, usually made of lead. Slugs offer improved accuracy and penetration, making them suitable for hunting larger game at extended distances. They are also favored by some law enforcement agencies for certain tactical situations.
It's important to note that there are specialized shotgun shells beyond these three main types. For example, there are less-lethal shotgun shells used by law enforcement for riot control. These shells typically contain rubber projectiles or bean bags designed to incapacitate without causing lethal harm.
When selecting shotgun shells, it's crucial to consider the intended use and the effectiveness required for the task at hand. Choosing the appropriate type of shotgun shell ensures optimal performance and increases the chances of a successful outcome. In the next section, we will explore how shotgun shells work and the firing process involved.
Choosing the Right Shotgun Shell
Choosing the right shotgun shell is crucial to ensure optimal performance and effectiveness in various shooting scenarios. In this section, we will explore the factors to consider when selecting shotgun shells, discuss the different sizes available, and provide recommendations for specific purposes.
1. Factors to Consider
a. Intended Use
Consider the purpose for which you will be using the shotgun. Are you planning to hunt birds, small game, or larger game? Are you using the shotgun for self-defense or target shooting? Different types of shotgun shells are designed to excel in specific situations, so understanding your intended use is essential in making the right choice.
b. Range
Consider the typical range at which you will be shooting. Some shotgun shells are optimized for close-range shooting, while others provide better performance at longer distances. Knowing the range of your shooting scenarios will help you select the appropriate shotgun shell for optimal results.
Photo source-(pexels.com)
c. Recoil
Recoil, or the backward movement of the shotgun after firing, can vary depending on the type of shotgun shell. Larger and more powerful shells tend to generate more recoil. Consider your comfort level with recoil and the impact it may have on your shooting accuracy and overall experience.
2. Shotgun Shell Sizes and What They Mean
Shotgun shells are categorized by gauge and shot size. Understanding the sizing system will help you select the right shotgun shell for your firearm:
a. Gauge
Shotgun shells are available in different gauges, with 12-gauge being the most common and widely used. Other popular gauges include 20-gauge and .410 bore. The gauge of your shotgun determines the size of the shotgun shell it can safely and effectively handle. Ensure that you match the gauge of the shotgun shell to the gauge of your shotgun.
b. Shot Size
Shotgun shells are also classified by shot size, denoted by numbers. Higher numbers indicate smaller shot sizes, while lower numbers indicate larger shot sizes. For example, #8 shot is smaller than #4 shot. The appropriate shot size depends on the intended use. Smaller shot sizes are suitable for small birds or clay shooting, while larger shot sizes are used for larger game or self-defense.
Photo source-(pexels.com)
3. Best Shotgun Shells for Different Purposes
a. Bird Hunting
For bird hunting, select shotgun shells with smaller shot sizes, such as #6 or #7.5, as they offer better pattern density for hitting fast-moving targets. Consider using shells specifically designed for upland game or waterfowl hunting, as they are tailored to those specific environments.
b. Small Game Hunting
When hunting small game, such as rabbits or squirrels, shotgun shells with slightly larger shot sizes, such as #4 or #5, provide better stopping power and penetration.
c. Deer Hunting
For deer hunting, consider using shotgun slugs or buckshot shells. Slugs offer increased accuracy and are suitable for longer-range shots, while buckshot provides multiple projectiles for close-range encounters. Check the regulations in your area regarding the use of slugs or buckshot for deer hunting.
d. Self-Defense
For self-defense purposes, consider using buckshot shells with larger shot sizes, such as 00 buck. These shells offer increased stopping power and are effective at close ranges.
Always consult local laws and regulations regarding the use of specific shotgun shells for hunting or self-defense purposes. Additionally, it is important to test different shotgun shells and patterns to determine which ones work best with your shotgun and meet your specific needs.
In the next section, we will discuss the safety guidelines and proper storage of shotgun shells to ensure safe handling and longevity.
Safety and Storage of Shotgun Shells
Ensuring the safety and proper storage of shotgun shells is essential for responsible firearm ownership. In this section, we will discuss guidelines for the safe handling of shotgun shells, the importance of proper storage, and the disposal of unused or old shotgun shells.
1. Safe Handling of Shotgun Shells
a. Follow Firearm Safety Rules
Adhere to the basic principles of firearm safety at all times. Treat every firearm as if it is loaded, keep your finger off the trigger until ready to shoot, never point the muzzle at anything you do not intend to shoot, and be aware of your target and what is beyond it.
b. Inspect Shells Before Use
Before loading a shotgun shell into your firearm, inspect it for any signs of damage or defects. Look for any cracks or deformities in the hull or casing, and ensure that the primer is intact. Discard any damaged shells.
c. Store Shells Separately
Keep your shotgun shells separate from your firearm, in a designated and secure location. This prevents accidental loading of shells into the firearm and adds an extra layer of safety.
d. Use Appropriate Ammunition
Always use the correct gauge and type of shotgun shells that are specifically designed for your shotgun. Using incorrect ammunition Photo source can lead to malfunctions or even catastrophic failures.
2. Proper Storage of Shotgun Shells
a. Store in a Cool and Dry Place
Shotgun shells should be stored in a cool, dry location to maintain their integrity. Exposure to extreme temperatures or moisture can potentially damage the shells and reduce their effectiveness.
b. Use Ammo Boxes or Containers
Consider storing your shotgun shells in dedicated ammo boxes or containers. These provide added protection and help keep the shells organized. Ensure that the containers are sturdy and properly labeled.
c. Separate Different Types of Shells
If you use multiple types of shotgun shells, it's advisable to keep them separated and clearly labeled. This prevents confusion and ensures that you grab the right shells for your intended purpose.
3. Disposal of Unused or Old Shotgun Shells
a. Do Not Dispose in Regular Trash
Shotgun shells should not be disposed of in regular household trash. They contain hazardous materials and can be dangerous if mishandled. Improper disposal can also lead to environmental contamination.
b. Contact Local Authorities or Range
Check with your local authorities, shooting ranges, or firearm dealers for guidance on proper disposal methods. They may have specific protocols in place for disposing of unused or old shotgun shells.
c. Seek Professional Assistance
If unsure about the proper disposal method, seek professional assistance. Local law enforcement agencies or ammunition manufacturers can provide guidance on how to safely dispose of shotgun shells.
By following the safety guidelines and storing shotgun shells properly, you can ensure the longevity of your ammunition and minimize any potential risks associated with mishandling. Responsible handling and storage play a vital role in maintaining a safe shooting environment.
In conclusion, understanding the different types of shotgun shells, how they work, and how to choose the right one for your purpose, along with prioritizing safety and proper storage, are essential aspects of responsible shotgun ownership. By applying this knowledge, you can enjoy the benefits of using a shotgun for various applications while ensuring the safety of yourself and others.
Enjoy this article? Leave a review below
Related articles
A Comprehensive Guide to Rifle Ammo
An Ultimate Guide to Hunting Rifles
Top Selling Rifle Optics For 2023
The Ultimate Buyer's Guide to Bullpup Rifles & Shotguns for [2023]